
Vitamins called nutrition vitamins are vital compounds that work as cofactors in many metabolic reactions within the body. They are important to the immune system and normal growth and development. Vitamin deficiencies can lead you to a host of health problems. They are therefore of great public health importance.
There are two basic types: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins. The urine is able to easily eliminate water-soluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored within the liver and tissues. Deficiency or excess of any one of these vitamins can lead to serious consequences.
Vitamins can be found in many foods. While some vitamins are naturally found, others can be manufactured in the body. Most vitamins are required for physiological processes. It is therefore necessary to consume a wide variety of foods to meet your daily requirements. Your doctor or dietitian can help you determine your nutrient needs. Another option is to consider taking a supplement.

The chemical properties and the ability of the molecule to dissolve in water, fat or other liquids determine the classification of vitamin. Vitamins are also classified by where they are transported, and the functions they perform in the body. Vitamin A is for example absorbed by carrier-dependent mechanisms in low concentrations.
It is becoming more important to pay attention to food-sourced vitamins. These studies have given insight into the metabolism of vitamins and the role of food in our health. Metabolic modifications of vitamins obtained from food can alter the structure or function of the vitamin. This can lead both to structural and major changes in the vitamin's chemical properties.
Depending on where a vitamin is located in the body, it can be classified into one of four categories: antioxidants, enzymes, hormones, and gene transcription elements. These four categories help to determine the health relevance of vitamins. Additionally, vitamins are involved in the production of a variety metabolic enzymes and hormones. One example is the methyl malonylcoenzyme CoA mutase, which plays a critical role in mammalian-cell metabolism.
Important connections have also been made between food-sourced vitamins and the bioavailability, or reversed epigenetic age. Vitamins are critical for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and steroid hormones, and for the formation of red blood cells. Vitamins may be taken either in plant- or animal-based forms.
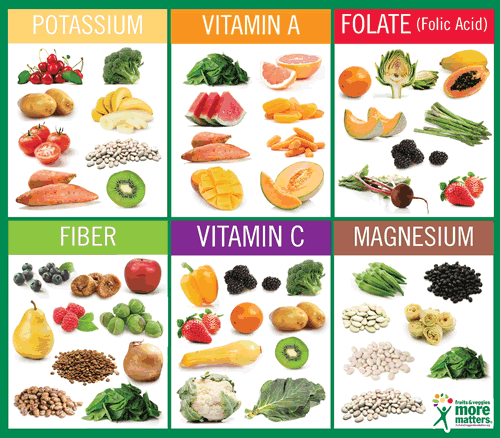
Vitamins are essential for protecting biological membranes from lipid oxidation. Vitamin E and selenium are involved in this process. Other vitamins can also be made endogenously by intestinal bacteria. Some vitamins are vital, while others are not. They are essential in small amounts, and come from many different sources.
The current food supply does not contain all the necessary vitamins. The recommended daily intake of vitamins will vary depending on the source of the vitamin and the gender. On average, an adult needs 60mg of vitamin D per day. Higher levels are required for older adults. Women need more iron in the premenopause.
FAQ
What is the difference between fat and sugar?
Fat is an energy source that comes from food. Sugar is a sweetener found in fruits, vegetables, and other foods. Both fats as well as sugars contain the same amount of calories. But fats are twice as calories as sugars.
Fats are stored in the body and contribute to obesity. They can cause cholesterol buildup which can lead to strokes and heart attacks.
Sugars provide instant energy and are rapidly absorbed by the body. This causes blood sugar levels to rise. High blood glucose levels can pose a danger because they increase the chance of developing type II Diabetes.
What can I do to boost my immune system?
There are trillions of cells in the human body. These cells combine to form organs or tissues that serve specific functions. Another cell takes its place when a cell dies. Cells communicate with one another using chemical signals called hormonal hormones. Hormones regulate all bodily functions from growth and developmental to metabolism and immunity.
Hormones can be described as chemicals produced by glands in the body. They are chemicals that travel through the bloodstream and function as messengers to control how our bodies work. Some hormones are produced in the body, while others are created outside.
Hormone production starts when hormone-producing cells release their contents into your bloodstream. Once hormones have been released, they travel through the body to their intended organ. Some hormones are only active for a brief time. Others hormones are more active and have a longer life expectancy. They can still influence the body's functions long after they have been eliminated from the bloodstream.
Some hormones are made in large quantities. Others are produced in small amounts.
Some hormones only are produced during certain periods of life. Estrogen is one example. It's produced in puberty, pregnancy and menopause. Estrogen aids women in developing breasts, maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. It helps to stimulate hair growth and maintains skin's softness.
How do you know what is best for you?
You need to listen to your body. Your body is the best judge of how much exercise, food and rest you should get. Your body will tell you what to do so that you don't go overboard. Be aware of your body and do what you can to keep it healthy.
Why does weight change as we age?
How can I tell if my bodyweight changes?
Weight loss occurs when there is less fat than muscle mass. This means that you must consume more calories than you use daily. Activity levels are the most common reason for weight loss. Other causes include illness, stress, pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and poor eating habits. When more fat is consumed than muscle mass, weight gain occurs. It happens when people eat more calories than they use during a given day. Overeating, increased physical activity and hormonal changes are all common reasons.
Our bodies lose weight because we eat fewer calories than we burn. Exercise regularly increases your metabolism rate, which allows you to burn more calories every day. However, this doesn't mean that we'll necessarily get thinner; what matters is whether or not we're losing fat or gaining muscle. If we are burning more calories than what we eat, then we will lose weight. But, if we consume more calories then we burn, then they are being stored as fat.
As we age, our ability to move around is slower and we are less mobile. We also tend to eat less food than we did when we were younger. This is why we tend to gain weight. However, our muscle mass is more important than our actual size.
Without weighing yourself each week, there is no way to know how much weight you have lost. There are many methods to measure your weight. You can also measure your waistline, your hips or your thighs. Some people prefer to use the bathroom scales, while some prefer to use tape measurements.
Track your progress by measuring your waistline and weighing yourself every week. You can also take images of yourself every few weeks to see how far it has come.
Online, you can find out your height and weight. You'd likely weigh 180 pounds if you were 5'10 tall and 180 pounds if you were 180lbs.
How does an anti-biotic work?
Antibiotics are drugs that destroy harmful bacteria. Antibiotics can be used to treat bacterial infection. There are many different types of antibiotics. Some can either be administered orally, while others may be injected. Other antibiotics can also be applied topically.
Antibiotics are often prescribed to people who have been exposed to certain germs. One example is if someone has had chickenpox and wants to prevent shingles. An injection of penicillin may be necessary to prevent pneumonia if someone has strep.
If antibiotics are to be administered to children, they must be prescribed by a doctor. Children are at greater risk than adults for developing serious side effects from taking antibiotics.
Diarrhea is one of the most common side effects of antibiotics. Other side effects include dizziness, nausea and vomiting, dizziness, stomach cramps, dizziness, allergic reactions, dizziness, dizziness, stomach cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, allergy, headaches, dizziness, dizziness, dizziness, stomach cramps, and stomach cramps. These side effects typically disappear once treatment is complete.
Exercise: Is it good or bad for immunity?
Your immune system is strengthened by exercise. Your body makes white blood cells that fight infections when you exercise. You also get rid toxins. Exercise helps prevent diseases like cancer and heart disease. It also reduces stress levels.
However, exercising too much can weaken your immune system. If you work out too hard, your muscles become sore. This can cause inflammation, swelling, and even death. Your body then has to produce more antibodies to fight off infection. Problem is, extra antibodies can trigger allergies and other autoimmune conditions.
So, don't overdo it!
How often do I need to exercise?
A healthy lifestyle requires regular exercise. There is no set time limit for exercising. Finding something that you love and sticking with it is the key.
It is a good idea to exercise at least three times per week. Then, you should aim to do between 20 and 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity. Moderate intensity means you'll still be breathing hard after you've finished. This type of workout burns around 300 calories.
Walking is a great option if you are a keen walker. You can do 10-minute walks four days per week. Walking is low-impact and easy on your joints.
Jogging is an alternative to running. You can do it for as little as 15 minutes each day. Running is a great way of burning calories and building muscle tone.
You can start slow if you are new to exercise. Begin by doing 5 minutes of cardio each day, a few times per week. Gradually increase your cardio time until you reach the goal.
Statistics
- In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake. (who.int)
- WHO recommends reducing saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake; reducing trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake; and replacing both saturated fats and trans-fats to unsaturated fats. (who.int)
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend keeping added sugar intake below 10% of your daily calorie intake, while the World Health Organization recommends slashing added sugars to 5% or less of your daily calories for optimal health (59Trusted (healthline.com)
External Links
How To
What does the term "vitamins" mean?
Vitamins are organic compounds found naturally in food. Vitamins are essential for our bodies to absorb nutrients from the foods we eat. Vitamins cannot come from the body so food must provide them.
There are two types: water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve quickly in water. You can find vitamin C,B1 or thiamine, B2 or riboflavin and B3 or niacin. B6 is pyridoxine. Folic acid, biotin and pantothenic are some examples. The liver and fatty tissue are the main storage places for fat-soluble vitamins. You can find vitamin D, E K, A and beta carotene as examples.
Vitamins can be classified according to biological activity. There are eight main groups of vitamins.
-
A - essential for normal growth and maintenance of health.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D – Essential for healthy teeth, bones and joints
-
E is required for good vision and reproduction.
-
K – Required for healthy muscles & nerves.
-
P – Vital for building strong bones.
-
Q - aids digestion, absorption and absorption iron
-
R – Required for making red blood vessels.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA), for vitamins, varies based on gender, age, and physical condition. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, (FDA), sets the RDA value.
For adults aged 19 and older, the RDA for vitamin B is 400 micrograms daily. For fetal development, pregnant women require 600 micrograms per daily. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Infants under one year of age require 700 micrograms per day, but this amount decreases to 500 micrograms per day between 9 months and 12 months of age.
Children ages 1-18years who are obese need 800 micrograms per day while those who are overweight need 1000 micrograms per day and children who are underweight need 1200 micrograms per day to meet their nutritional needs.
Children 4-8 years old with anemia will need 2200 mg of vitamin D daily.
2000 micrograms is the minimum daily intake for general health in adults older than 50 years. Breastfeeding or pregnant women require 3000 micrograms per daily due to higher nutrient demands.
1500 micrograms is the recommended daily intake for adults aged 70+, as they lose 10% of their muscle every ten years.
Women who have been pregnant or are lactating require more than the RDA. Pregnant woman need 4000 micrograms daily in pregnancy and 2500 per day after childbirth. Breastfeeding mothers require 5000 micrograms daily when breast milk production is occurring.