
Good infant nutrition is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, regular development, and good health during the first 3 years. Healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and consuming healthy foods can help reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. A healthy diet and lifestyle in the early years can make a difference for your child's growth and development.
It is important to remember that each baby has a different nutritional needs. There are four major food groups: carbohydrates and fats, protein, vitamins, and proteins. The best source of nutrients for young children is breast milk. Breastfeeding is an option but infant formula can also be beneficial. Breast milk has many nutrients that can help your baby build an immune system.
Foods should have at least four calories per grams and be energy dense. Young children need a variety in food types to help them grow. A regular meal and snack schedule is important for your child. Drinking water should be something you do often for your child to quench his thirst. You can seek advice from a dietitian to help you make informed choices about what foods you should be serving your child.

Some foods, such as fruits, can cause choking problems. However, it is best to introduce new foods to your child one at a while. Rice cereal can be mixed with breastmilk or formula. After your baby is able hold his/her head up and can sit upright, you can transition to solid food. These can be pureed, lumpy, or mashed.
Your child's growth should also be tracked by a dietitian. To help you decide if your child is getting enough food, you will need to know the following information: Your child's height and weight. The Dietitians of Canada can help you determine your child's nutritional needs and recommend ways to increase your child's intake.
Another resource worth considering is The Child of Mine. This book focuses on health benefits associated with eating a variety if foods. It is a wonderful way to encourage your child towards healthy eating. You can also discuss the food groups with your child by having them play with toys that match their age. Encourage your child to eat small portions of food.
It is important to remember that your child must be aware of his or her hunger cues when choosing food for him/her. Your child should be fed every two to three hours, and a variety of nutritious foods should be offered. They should be eaten in moderation with very little sugar or added salt.
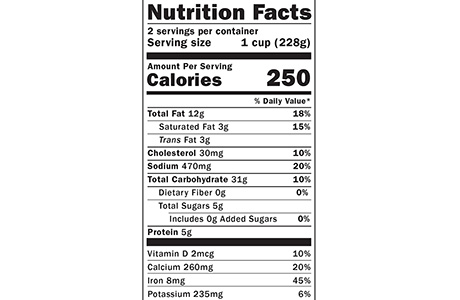
Your infant's nutrition should include iron. It is a good idea to start with iron-rich cereals and meat alternatives, then move on to other foods.
FAQ
What can you do for your immune system to improve?
The human body consists of trillions of cells. These cells combine to form organs or tissues that serve specific functions. One cell is replaced by another when it dies. Cells communicate with one another using chemical signals called hormonal hormones. Hormones control all bodily functions, including growth, development, metabolism, immunity and immune system.
Hormones are chemical substances that glands secrete throughout the body. They are messengers that help control how our bodies operate. Some hormones can be produced within the body while others can be made outside.
Hormone production starts when hormone-producing cells release their contents into your bloodstream. Once hormones are released they move through the bloodstream until reaching their target organ. Sometimes hormones stay active for only a short time. Others hormones are more active and have a longer life expectancy. They can still influence the body's functions long after they have been eliminated from the bloodstream.
Some hormones can only be produced in large quantities. Others are made in very small amounts.
Certain hormones can only be produced at specific times in life. For instance, estrogen is produced during puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and old age. Estrogen helps women develop breasts, maintain bone density, and prevent osteoporosis. It also promotes hair growth and keeps skin smooth and soft.
Why is it so important to lead a healthy lifestyle
Healthy lifestyles lead to happier and longer lives. Healthy eating habits, regular exercise, healthy sleep habits, stress management, and good sleep habits can help to prevent heart disease, stroke, diabetes, cancer, and other serious diseases.
A healthy lifestyle will also improve our mental health by helping us cope better with everyday stresses. A healthy lifestyle will help you feel more confident and younger.
What should I eat?
You should eat lots of vegetables and fruits. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and help to strengthen your immune system. Vegetables and fruits are high in fiber which helps to digest and fill you up. Aim to eat five to six servings of fruit or veg each day.
Water is essential for your body. Water flushes toxins out of the body and helps to feel full between meals. Drink about eight glasses each day.
Eat whole grains instead of refined ones. Whole grains contain all of their nutrients, including B vitamins and iron. Some nutrients have been removed from refined grains.
Sugary drinks should be avoided. Sugary drinks are high in empty calories and can lead to obesity. Instead, opt for water, milk, or unsweetened tea.
Avoid fast food. Fast food has very little nutritional value. Fast food may be delicious, but it will not give you the energy that you need to perform your tasks properly. Instead, stick to healthier options like soups and sandwiches, pasta, and salads.
Reduce your alcohol intake. Alcohol is a poor nutrient and has empty calories. Limit your intake to two alcoholic drinks per week.
Reduce red meat intake. Red meats can be high in cholesterol and saturated fat. You should choose lean cuts like beef, pork lamb, chicken and fish instead.
Statistics
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- nutrients.[17]X Research sourceWhole grains to try include: 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, brown rice, whole grain oats, farro, millet, quinoa, and barley. (wikihow.com)
- In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake. (who.int)
- WHO recommends reducing saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake; reducing trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake; and replacing both saturated fats and trans-fats to unsaturated fats. (who.int)
External Links
How To
What does "vitamin" actually mean?
Vitamins are organic substances found naturally in food. Vitamins allow us to absorb nutrients from food. The body cannot make vitamins; therefore, they must be obtained from food.
Two types of vitamins exist: water soluble and oil soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve readily in water. Examples include vitamin C,B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B6 (pyridoxine), folic acid, biotin, pantothenic acid, and choline. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored within the liver and in fatty tissue. Vitamin D, E, K and A are some examples.
Vitamins can be classified according to biological activity. There are eight major groups of vitamins:
-
A - Vital for healthy growth.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D - Vital for healthy bones and teeth
-
E is required for good vision and reproduction.
-
K - Required for healthy nerves and muscles.
-
P - essential for strong bones, teeth and tendons
-
Q - aids digestion, absorption and absorption iron
-
R - necessary for making red blood cells.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA), for vitamins, varies based on gender, age, and physical condition. RDA values are set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
For adults aged 19 or older, the RDA of vitamin A is 400mg per day. Pregnant mothers need 600 micrograms a day to ensure fetal growth. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Infants under one year of age require 700 micrograms per day, but this amount decreases to 500 micrograms per day between 9 months and 12 months of age.
Children between the ages of 1-18 need 800 micrograms per daily for obesity, while those overweight require 1000 micrograms. To meet their nutritional needs, children underweight and obese need 1200micrograms.
Children 4-8 years old with anemia will need 2200 mg of vitamin D daily.
Adults over 50 years of age need 2000 micrograms per day for general health. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need 3000 micrograms per day due to increased nutrient requirements.
Adults over 70 years of age need 1500 micrograms per day since they lose about 10% of their muscle mass each decade.
Women who have been pregnant or are lactating require more than the RDA. Pregnant and breastfeeding women require 4000 micrograms each day during pregnancy and 2500 Micrograms each day after birth. Breastfeeding mothers need 5000 micrograms per day when breast milk is being produced.