
Dietary guidelines, which are science-based nutrition recommendations, help Americans reduce their chances of developing chronic diseases. The US Department of Agriculture (USDA), and US Department of Health and Human Services(HHS) publish these guidelines approximately every five year. These guidelines are a reliable source of information for educators and health professionals as well as the general public. It is also used as a foundation for federal nutrition and food programs.
Dietary guidelines are updated by the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. The Committee is composed of leading health experts who assess the strength of the evidence and determine which recommendations to make. When a new edition is released, it reflects the most current scientific knowledge. Currently, the DGA recommends a diet low in saturated fat and calorie-dense foods, such as vegetables and fruits. To reduce dietary fat intake, the Guidelines recommend that saturated fat be replaced with polyunsaturated. The Guidelines also eliminate the upper limit of total dietary cholesterol.
Others recommend healthy eating habits, such as high intakes of fruits, vegetables, and seafood. Additionally, healthy eating patterns are marked by a lower intake of added sugars and refined grains as well as a lower level of saturated fat. It is best to choose a moderately high-sugar diet for people with diabetes. People who live a sedentary life should get more exercise.

The guidelines for dietary intake encourage a diet rich with fiber, whole grains, and other whole grains. They also encourage people to eat fruits and vegetables daily. This is particularly important for adolescents and children.
The DGA's current recommendations were based on the latest advances in nutrition science and food technology. The industry has attempted to change these guidelines. Recent research has shown that the food sector spent more than ten thousand dollars lobbying against DGA’s recommendations. Some experts have criticized this decision, calling it an override on the scientific evidence.
The dietary guidelines can be used as a reference tool for both the public and health professionals. These guidelines can be considered evidence-based because they are based upon a range of studies. These Guidelines can be used to teach public health professionals.
To keep up with scientific advances and new findings, dietary guidelines are continuously updated. The Guidelines are designed to reduce overweight and obesity, as they also help to reduce the risk for chronic diseases.
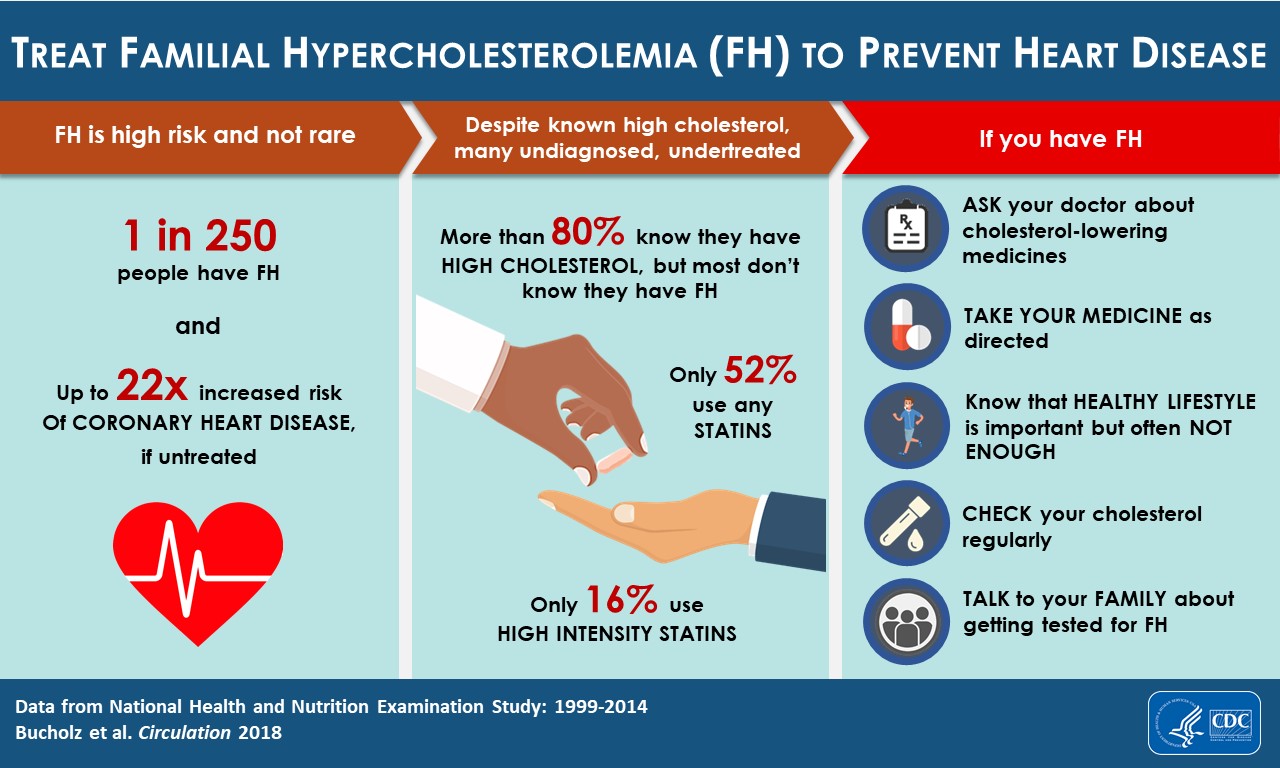
The Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee regularly updates the 2010 Dietary Guidelines to Americans. DHHS received input from nutrition and medical experts as well as members of the general public. Following this, the Committee reviewed existing scientific evidence before releasing a final report. The Advisory Committee issued 29 recommendations to the U.S. populace from this report. These recommendations include limiting sodium, saturated and processed fats, sugar, calories, and avoiding excess calories. The Pyramid also suggests that people eat a diet low on total fat, saturated and cholesterol.
Another concern is the presence of added sugars in sugar-sweetened beverages, processed foods, and other food products. The Dietary Guidelines recommend reducing the amount of added sugars to 2,300 mg per day. Additionally, guidelines recommend that individuals who consume alcohol not exceed one drink per week. There is a higher chance of injury from alcohol so it is recommended for those who are legal drinking age to limit their alcohol intake.
FAQ
How do I find out what's best for me?
You must listen to your body. When it comes to your body's needs for exercise, food, or rest, it is the best. It's important to pay attention to your body so you don't overdo things. Listen to your body and make sure you're doing everything you can to stay healthy.
Does being cold give you a weak immune system?
There are two types: those who love winter, and those who don't. It doesn't matter if you love it or not, it is possible to wonder why it makes you feel so miserable when it gets cold outside.
Our bodies were designed to work best in warm climates. We evolved to thrive in hot environments because of the abundance of food resources.
Today's environment is vastly different from the one our ancestors experienced. We spend a lot more time indoors, and are more likely to be exposed to extreme temperatures like heat and cold.
This means that our bodies aren’t used to these extremes. That means that when we do venture outdoors, we're left feeling tired, sluggish, and even sick.
There are many ways to avoid these side effects. The best way to avoid these problems is to ensure that your body stays hydrated throughout the day. Drinking plenty of water will help you keep your body hydrated and flush out toxins.
It is important to eat healthy foods. Healthy food will help your body maintain its optimal temperature. This is particularly helpful for anyone who spends long periods of time inside.
It is worth taking a few extra minutes each day to meditate. Meditation helps you relax your mind and body, which makes it easier to deal with stress and illness.
Do I need calories to count?
It is possible to wonder "what the best diet is for me?" or "is counting calories necessary?" The answer to this question depends on many factors, including your current health, your personal goals and preferences, as well as your overall lifestyle.
The Best Diet for me - Which One Is Right for You?
The best diet for me depends on my current health status, my personal goals, my preferences, and my overall lifestyle. There are many different diets, some good, some not. Some work well for certain people while others don't. What can I do to make the right choice? What should I do?
This article aims at answering these questions. The article starts by introducing the many types of diets currently available. Next, we will discuss the pros & cons of each kind of diet. We'll then discuss how to choose which one is best for you.
Let's first take a look at different diets.
Diet Types
There are three types of diets available: ketogenic, high-protein, and low-fat. Let's discuss them briefly below.
Low Fat Diets
A low-fat diet is one that limits the intake of fats. This is achieved by reducing saturated fat intake (butter, cream cheese etc.). These fats can be replaced with unsaturated fats like avocados and olive oil. People who are looking to lose weight quickly and easily will benefit from a low-fat diet. However, constipation, stomach pain, and heartburn can all be caused by this type of diet. A person may also experience vitamin deficiencies if they don't get enough vitamins.
High Protein Diets
High-protein diets limit carbohydrates and favor proteins. These diets have higher protein levels than other diets. They are meant to help build muscle mass and burn more calories. However, they might not provide enough nutrition for those who need to eat frequently. They can also be very restrictive so they may not be suitable for everyone.
Ketogenic Diets
These diets are also known under the name keto diets. They are high in fat and moderate in protein and carbs. They are commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders as they allow them to train harder, longer and without feeling fatigued. They do require strict compliance to avoid any side effects like fatigue, headaches, nausea, and headaches.
What is the difference of fat and sugar?
Fat can be a source of energy that is obtained from food. Sugar is a sweetener found in fruits, vegetables, and other foods. Both fats and sugars provide the same number of calories. But fats are twice as calories as sugars.
Fats can be stored in the body, which can lead to obesity. They can lead to cholesterol buildup in the arteries, which could cause heart attacks or strokes.
Sugars are quickly absorbed by the body and provide instant energy. This causes blood glucose to rise. High blood glucose levels can be dangerous because it increases the risk of developing type II diabetes.
Why is it so important to lead a healthy lifestyle
Healthy lifestyles lead to happier and longer lives. Regular exercise, healthy eating habits, healthy sleep habits and stress management can all help prevent strokes, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
A healthy lifestyle can also help improve mental health and make it easier to deal with everyday stressors. A healthy lifestyle will increase self confidence, and it will make us feel younger.
What are the 7 keys to a healthy, happy life?
-
You should eat right
-
Exercise regularly
-
Good sleep
-
Drink lots of water
-
Get enough rest
-
Happy!
-
Smile often
How to measure bodyfat?
A Body Fat Analyzer is the best way to measure body weight. These devices are used to determine the body's percentage for people who want weight loss.
Statistics
- nutrients.[17]X Research sourceWhole grains to try include: 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, brown rice, whole grain oats, farro, millet, quinoa, and barley. (wikihow.com)
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- WHO recommends reducing saturated fats to less than 10% of total energy intake; reducing trans-fats to less than 1% of total energy intake; and replacing both saturated fats and trans-fats to unsaturated fats. (who.int)
- In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake. (who.int)
External Links
How To
What does the term "vitamins" mean?
Vitamins are organic compounds naturally found in food. Vitamins aid us in absorbing nutrients from the food we eat. Vitamins are not made by the body, so they must be obtained through food.
There are two types of vitamins: water soluble and fat soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve easily when they are dissolved in water. Some examples include vitamin C,B1 and B2 vitamins (thiamine), B2 and riboflavin, B3 and niacin, B6 vitamins (pyridoxine), B6 vitamins (niacin), folic acids, biotin, pantothenic acids, and Choline. The liver and fatty tissue are the main storage places for fat-soluble vitamins. You can find vitamin D, E K, A and beta carotene as examples.
Vitamins are classified according to their biological activity. There are eight main groups of vitamins.
-
A - vital for normal growth and maintaining good health.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D - necessary for healthy bones and teeth.
-
E is required for good vision and reproduction.
-
K - essential for healthy nerves, muscles, and joints.
-
P - vital for building strong bones andteeth.
-
Q - Aids in digestion and absorption.
-
R - Red blood cells are made from red blood cells.
The recommended daily allowance for vitamins (RDA) varies according to age, gender, or physical condition. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets the RDA values.
For adults aged 19 and older, the RDA for vitamin B is 400 micrograms daily. Pregnant mothers need 600 micrograms a day to ensure fetal growth. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. For infants younger than one year, 700 micrograms are required daily. However, this number drops to 500 micrograms each day for children aged 9-12 months.
Children aged 1-18 years need 800 micrograms daily, while children overweight require 1000 micrograms per days. Children who are severely obese or underweight will need 1200 micrograms each day.
Children ages 4-8 years who have been diagnosed with anemia need 2200 micrograms per day of vitamin C.
Adults over 50 years of age need 2000 micrograms per day for general health. Due to their increased nutrient needs, pregnant and breastfeeding women need 3000 micrograms daily.
Adults over 70 years of age need 1500 micrograms per day since they lose about 10% of their muscle mass each decade.
Women who are pregnant and lactating need more nutrients than the RDA. Pregnant and breastfeeding women require 4000 micrograms each day during pregnancy and 2500 Micrograms each day after birth. Breastfeeding mothers need 5000 mg per day when breastmilk is being produced.