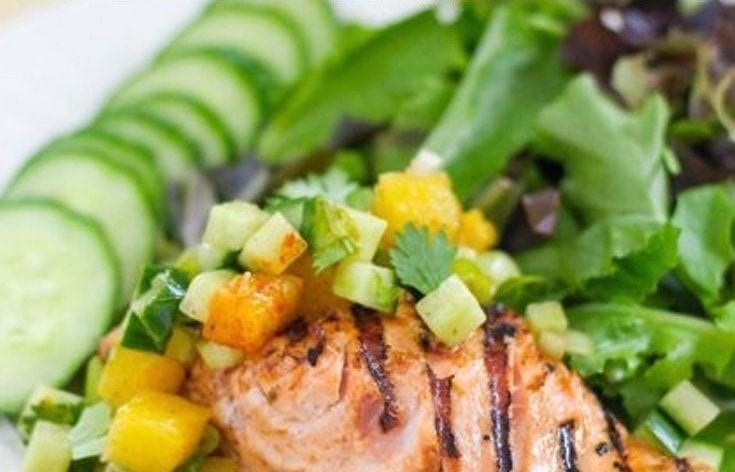

For athletes to be able to perform at their best, they need a wide range of nutrients. A meal plan that is well designed can help athletes stay healthy while still allowing for optimal performance.
Regardless of the sport an athlete engages in, there are general guidelines to follow when preparing a diet. Most important is to eat enough carbs and protein. These are two important macronutrients that provide an essential source of energy for the human body.
Aside from carbohydrates, fats can also be a vital source of energy. Fats are vital for biological functions like hormone regulation and are used to support the recovery of muscle tissue. They can also increase hunger pangs. While some athletes may believe that fat makes you fat, it is important to realize that your body can also use fat as an energy source.
An effective diet for athletes should contain sufficient carbohydrates and protein, as well as a low fat percentage. Below are some resources that provide information about nutrition for sports.
The diets of athletes must include adequate water intake. This is particularly important for athletes who participate in endurance sports. An athlete's mental clarity can be affected, and their performance may suffer. Athletes must hydrate prior and during exercise.
Fluid supplementation is important for proper nutrition and maintaining a healthy temperature. The ideal diet for an athlete should include foods rich in nutrients such as whole grains or fruits. Sportsmen and women who eat foods high in nutrients can receive essential vitamins, minerals, as well as enzymes.
Protein is a vital component of an athlete's diet, as it plays a role in muscle growth and repair. It is important to eat a variety of protein-rich foods, such as meat, fish, dairy products, nuts and eggs. Athletes need to ensure they are getting the right kinds of protein for their individual needs.
It's crucial to plan your meals ahead of time when it comes down to nutrition. This is best done by creating a daily menu plan. Talk to a professional about how to do this.
The type of exercise an athlete does will determine the energy source they use. At the end of the day, carbohydrates are the most important source for energy. Athletes who train hard should consume 70% or more of their daily calories from carbohydrates. As a rule of thumb, an athlete should eat 0.5 grams of carbohydrate for every pound of their body weight.

Athletes need to eat a balanced meal that includes carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Alcohol should be avoided. It is important to avoid alcohol while training. Athletes can also benefit from limiting alcohol intake as they are high in calories.
Apart from carbohydrates, it is important to consume a variety fruits and vegetables. These can prevent illness and promote good health. A wide range of antioxidants are found in fruits and vegetables.
FAQ
Why should we have a healthy lifestyle to begin with?
Living a healthy lifestyle can help you live longer and more happy lives. Good nutrition, exercise regularly, good sleep habits, and stress control can help you avoid diseases such as heart disease and stroke.
A healthy lifestyle will also improve our mental health by helping us cope better with everyday stresses. Having a healthy lifestyle will also boost our self confidence and help us look and feel younger.
How much should I weight for my height and age? BMI calculator & chart
Use a BMI calculator to determine how much weight is needed to lose. Healthy BMI ranges between 18.5 to 24.9. Aim to lose 10 pounds per month if your goal is to lose weight. Enter your height and weight to calculate your BMI.
Check out this BMI chart to determine if you are overweight or obese.
What is the best food for me?
Your lifestyle and individual needs will determine the best diet for your body. Consider how much energy and low-calorie foods you consume, as well as whether or not you are a fan of fruits and vegetables.
If you are trying to lose weight, then you may want to try intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting allows you to consume only specific meals throughout your day rather than three large meals. This might be better than traditional diets that have daily calorie counts.
Research suggests that intermittent fasting may increase insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. This can result in improved blood sugar levels as well as a lower risk of developing diabetes. Some research also suggests that intermittent fasting might promote fat loss, and improve overall body composition.
What's the difference between fat/sugar?
Fat is an energy source that comes directly from food. Sugar is a sweetener found in fruits, vegetables, and other foods. Both sugars, and fats, have the same calories. But fats are twice as calories as sugars.
Fats are stored in the body and contribute to obesity. They can lead to cholesterol buildup in the arteries, which could cause heart attacks or strokes.
Sugars are quickly absorbed into the body and provide instant fuel. This causes blood glucose levels in the body to rise. High blood glucose levels can lead to type II diabetes.
Do I need calories to count?
You might be asking "What is the best diet?" or "is counting calories necessary?" This depends on several factors like your current health and personal goals. Your preferences and overall lifestyle.
Which one is right for you?
My personal health, goals, lifestyle and preferences will all influence the best diet. There are many diets available, some good and others not so good. Some diets work better than others. What should I do? What should I do?
These are the questions this article will answer. It begins with an overview of the different diets today. Next, we'll discuss the pros and cons for each type of diet. Finally, we'll discuss how to select the best one.
Let's look at some of the main types of diets to get started.
Diet Types
There are three types of diets available: ketogenic, high-protein, and low-fat. Let's talk about them briefly.
Low Fat Diets
A low-fat diet is a diet that reduces the amount fats consumed. This is achieved through a reduction in saturated fats (butter or cream cheese), etc. These fats can be replaced with unsaturated fats like avocados and olive oil. A low fat diet is often recommended for those who want to lose weight quickly and easily. However, constipation, stomach pain, and heartburn can all be caused by this type of diet. It can also lead to vitamin deficiencies, if someone doesn't get enough vitamins in their food.
High Protein Diets
High-protein diets limit carbohydrates and favor proteins. These diets often have higher levels of protein than most other diets. They can help you build muscle mass, and also burn more calories. The downside is that they may not provide adequate nutrition for someone who needs to eat regularly. They are not suitable for all people because they can be restrictive.
Ketogenic Diets
These diets are also known under the name keto diets. They are high in fat, moderately high in protein, and low in carbohydrates. They are commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders as they allow them to train harder, longer and without feeling fatigued. To avoid side effects such as fatigue, nausea, headaches, or other unpleasant side effects, you must strictly adhere to their instructions.
Increase immunity with herbs or supplements
To boost immunity function, herbs and natural remedies are available. Some common examples include garlic, ginger, oregano oil, echinacea, ginkgo biloba, and vitamin C.
These herbs should not be considered as a substitute for conventional medical treatment. They may cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, headaches, dizziness, and allergic reactions.
Statistics
- nutrients.[17]X Research sourceWhole grains to try include: 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, brown rice, whole grain oats, farro, millet, quinoa, and barley. (wikihow.com)
- WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. (who.int)
- According to the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, we should strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity each week (54Trusted Source Smoking, harmful use of drugs, and alcohol abuse can all seriously negatively affect your health. (healthline.com)
- According to the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, a balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy and whole grains is needed for optimal energy. (mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
External Links
How To
What does "vitamin" actually mean?
Vitamins can be described as organic compounds found in food. Vitamins aid us in absorbing nutrients from the food we eat. Vitamins cannot be produced by the body. They must be obtained from food.
There are two types vitamins: water soluble or fat soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve quickly in water. These include vitamin C (thiamine), Vitamin B1 (riboflavin), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), Vitamin C, B1 (thiamine), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), and Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). The liver and fatty tissues are home to fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamin D, E, K and A are some examples.
Vitamins are classified based on their biological activity. There are eight main types of vitamins:
-
A - Vital for healthy growth.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D - Essential for healthy teeth and bones.
-
E - required for good vision & reproduction.
-
K - Required for healthy nerves and muscles.
-
P – Vital for building strong bones.
-
Q - aids digestion, absorption and absorption iron
-
R – Required for making red blood vessels.
The recommended daily allowance for vitamins (RDA) varies according to age, gender, or physical condition. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration sets RDA values.
For example, the RDA for vitamin A is 400 micrograms per dayfor adults 19 years or older. However, pregnant women need 600 micrograms per day because it is important for fetal development. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Babies under one-year old need 700 micrograms per daily. Between 9 and 12 month, however, this drops to 500 mg per day.
Children aged between 1-18 years old who are obese require 800 micrograms per Day, while overweight children need 1000 micrograms every day. Children underweight or obese will require 1200 micrograms a day to meet their nutritional requirements.
Children ages 4-8 years who have been diagnosed with anemia need 2200 micrograms per day of vitamin C.
2000 micrograms are required daily for good health in adults over 50. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need 3000 micrograms per day due to increased nutrient requirements.
Adults over 70 years of age need 1500 micrograms per day since they lose about 10% of their muscle mass each decade.
Women who are pregnant and lactating need more nutrients than the RDA. Pregnant women require 4000 micrograms daily during pregnancy, and 2500 micrograms every day after birth. Breastfeeding mothers need to consume 5000 micrograms each day when breastmilk has been produced.